Understanding Facultative Organisms: The Adaptable Lifeforms
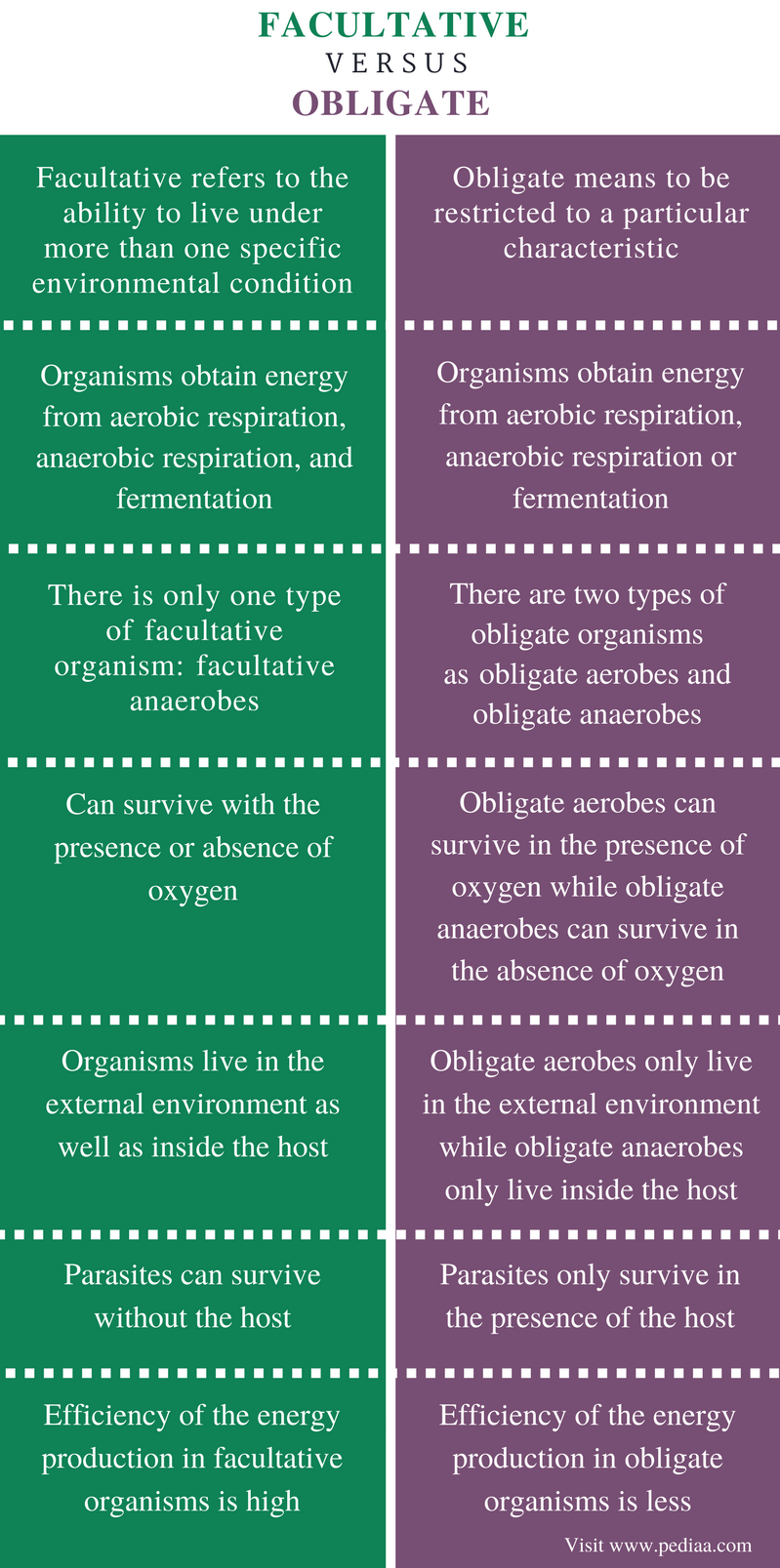
Facultative organisms are fascinating entities within the biological world that showcase remarkable adaptability. These organisms have the unique ability to thrive in a variety of environments, whether aerobic or anaerobic, allowing them to exploit a range of ecological niches. This versatility is not only crucial for their survival but also plays a significant role in various ecosystems. From bacteria to certain plants and animals, facultative organisms demonstrate an incredible capacity to adjust their metabolic processes according to the availability of oxygen. Their presence is vital for maintaining ecological balance and promoting biodiversity.
The importance of facultative organisms extends beyond their survival strategies; they also contribute to essential biochemical processes. For instance, they are involved in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and energy flow within ecosystems. Their ability to switch between different metabolic pathways allows them to perform critical functions, such as breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients, which in turn supports other life forms. Understanding the role of facultative organisms is key to appreciating the complexity of life on Earth.
In this article, we will explore the characteristics of facultative organisms, their significance in various ecosystems, and how they differ from obligate organisms. By delving into the world of these adaptable lifeforms, we can gain insights into their contributions to our environment and the fascinating ways they navigate the challenges of survival.
What are Facultative Organisms?
Facultative organisms are those that can adapt to different environmental conditions, particularly in terms of oxygen availability. They can live in both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) conditions, allowing them to survive in diverse habitats. This adaptability is a key characteristic that sets them apart from obligate organisms, which require specific conditions to thrive.
How Do Facultative Organisms Survive in Different Conditions?
Facultative organisms employ various metabolic pathways to generate energy depending on the oxygen levels present. For example, in aerobic conditions, they use cellular respiration to efficiently produce energy. However, in anaerobic conditions, they switch to fermentation or anaerobic respiration, allowing them to continue thriving even without oxygen. This metabolic flexibility is crucial for their survival and success in fluctuating environments.
What Are Some Examples of Facultative Organisms?
- Yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae can ferment sugars in anaerobic conditions or respire in the presence of oxygen.
- Bacteria: E. coli can switch between aerobic respiration and fermentation based on the availability of oxygen.
- Plants: Certain species can adapt their respiration methods depending on soil conditions.
Why Are Facultative Organisms Important in Ecosystems?
Facultative organisms play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Their ability to thrive in different conditions enables them to contribute to nutrient cycling, decomposition, and energy flow. By breaking down organic matter, they help recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, supporting plant growth and overall biodiversity.
How Do Facultative Organisms Contribute to Biochemical Processes?
Facultative organisms are involved in several essential biochemical processes, including:
- Nutrient cycling: They help decompose organic materials, returning nutrients to the soil.
- Energy flow: Their metabolic activities contribute to the overall energy dynamics of ecosystems.
- Soil health: Their presence can improve soil structure and fertility, benefiting plant growth.
What Are the Differences Between Facultative and Obligate Organisms?
While both facultative and obligate organisms are essential for ecosystem function, they differ significantly in their adaptability:
- Facultative organisms can thrive in a variety of conditions, while obligate organisms require specific environments.
- Facultative organisms can switch metabolic pathways, whereas obligate organisms have fixed metabolic processes.
- Facultative organisms can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, while obligate organisms are restricted to one.
What Challenges Do Facultative Organisms Face?
Despite their adaptability, facultative organisms face several challenges that can impact their survival. Environmental changes, such as pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction, can alter the conditions they depend on. Additionally, competition with other species and the availability of resources can affect their populations. Understanding these challenges is essential for conservation efforts aimed at protecting biodiversity.
How Can We Study Facultative Organisms?
Research on facultative organisms can be conducted through various methods, including:
- Laboratory experiments to observe metabolic changes under different oxygen conditions.
- Field studies to assess their roles in natural ecosystems.
- Genetic analysis to understand the mechanisms behind their adaptability.
What Is the Future of Research on Facultative Organisms?
The study of facultative organisms is crucial for understanding ecological dynamics and developing strategies for biodiversity conservation. Future research may focus on their responses to climate change, their roles in ecosystem services, and their potential applications in biotechnology. By exploring the fascinating world of facultative organisms, we can gain valuable insights into the resilience of life on Earth.