Understanding Torque Units In Physics: A Comprehensive Guide
Torque is an essential concept in physics, playing a fundamental role in mechanics and engineering. It is the measure of the rotational force applied to an object, which can influence its motion and stability. Understanding the various torque units physics is crucial for professionals in fields such as engineering, automotive design, and physics education. By grasping the principles behind torque, one can better appreciate how forces interact in our everyday lives.
In the realm of physics, torque is expressed in several units, with each serving a specific purpose depending on the context. The most commonly used torque units include Newton-meters (Nm), pound-feet (lb-ft), and kilogram-meters (kg-m). These units allow scientists and engineers to quantify and communicate the effects of rotational forces accurately. However, the selection of the appropriate unit can sometimes be confusing, especially for those who are new to the subject.
This article aims to demystify torque units in physics by exploring their definitions, applications, and conversions. Whether you're a student looking to enhance your understanding or a professional seeking to refine your knowledge, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the world of torque. We will cover essential questions surrounding torque units physics, ensuring you leave with a solid grasp of the topic.
What is Torque in Physics?
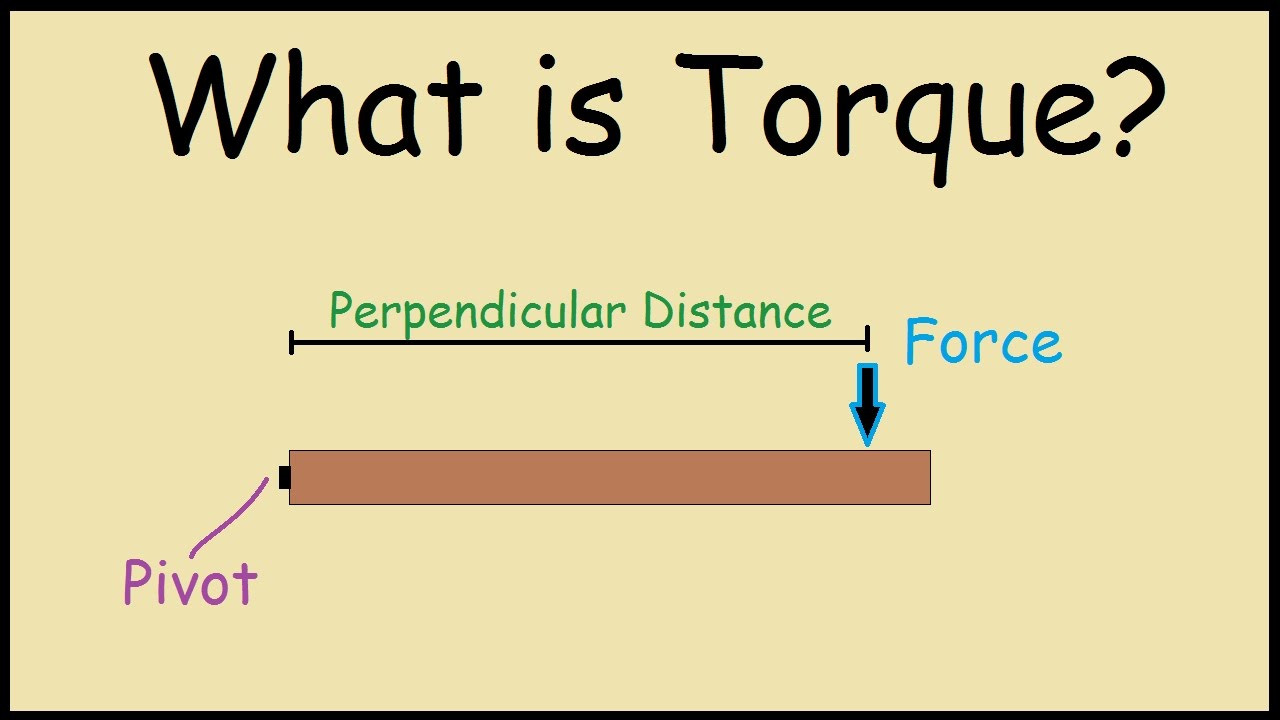
Torque, often represented by the Greek letter tau (τ), is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate. It is the rotational equivalent of linear force and is defined mathematically as:
τ = r × F
Where:
- τ is the torque
- r is the distance from the pivot point to the point where the force is applied (also known as the lever arm)
- F is the applied force
Why Are Torque Units Important in Physics?
Understanding torque units is essential for several reasons:
- Precision in Calculations: Different applications may require different units, and using the correct unit ensures accuracy in calculations.
- Standardization: Common units allow for consistent communication and understanding across various fields and disciplines.
- Real-World Applications: Knowledge of torque units is vital in fields such as automotive engineering, construction, and robotics.
What Are the Most Common Torque Units in Physics?
Torque can be measured in various units, each with its specific applications:
- Newton-Meters (Nm): The SI unit of torque, commonly used in scientific and engineering contexts.
- Pound-Feet (lb-ft): Often used in the United States, especially in automotive specifications.
- Kilogram-Meters (kg-m): A less common unit, but still relevant in certain engineering applications.
How Do You Convert Between Torque Units?
Converting between torque units is a straightforward process, but it requires understanding the relationships between different units. Here are some common conversions:
- 1 Nm = 0.73756 lb-ft
- 1 lb-ft = 1.35582 Nm
- 1 Nm = 0.10197 kg-m
- 1 kg-m = 9.80665 Nm
What Factors Affect Torque in Physics?
Several factors can influence the amount of torque generated on an object:
- Magnitude of the Force: The greater the force applied, the more torque is produced.
- Distance from the Pivot Point: Increasing the lever arm distance will result in greater torque.
- Angle of Application: Torque is maximized when the force is applied perpendicular to the lever arm.
How is Torque Measured in Practical Applications?
In real-world applications, torque is typically measured using specialized tools such as:
- Torque Wrenches: Used to apply a specific torque to fasteners, critical in automotive and construction work.
- Torque Sensors: Devices that measure torque in machinery and equipment for monitoring and control purposes.
- Dynamometers: Instruments used to measure force and torque in engine testing and research.
What Are Some Real-World Examples of Torque?
Torque plays a significant role in various everyday situations:
- Tightening Bolts: Applying torque correctly ensures fasteners are secured without over-tightening.
- Opening a Door: The further away you push from the hinge, the easier it is to open the door.
- Driving a Screw: The torque applied helps to drive the screw into the material without stripping it.
Conclusion: Mastering Torque Units in Physics
In summary, torque is a vital concept in physics that is measured using various units. Understanding torque units physics is essential for anyone engaged in the fields of science, engineering, or mechanics. By grasping the principles of torque, including its definition, unit conversions, and applications, you can apply this knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios. Whether you're working on a car, constructing a building, or simply understanding the forces around you, mastering torque units will enhance your comprehension of the physical world.