Understanding Leukoplakia From Chewing Tobacco: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
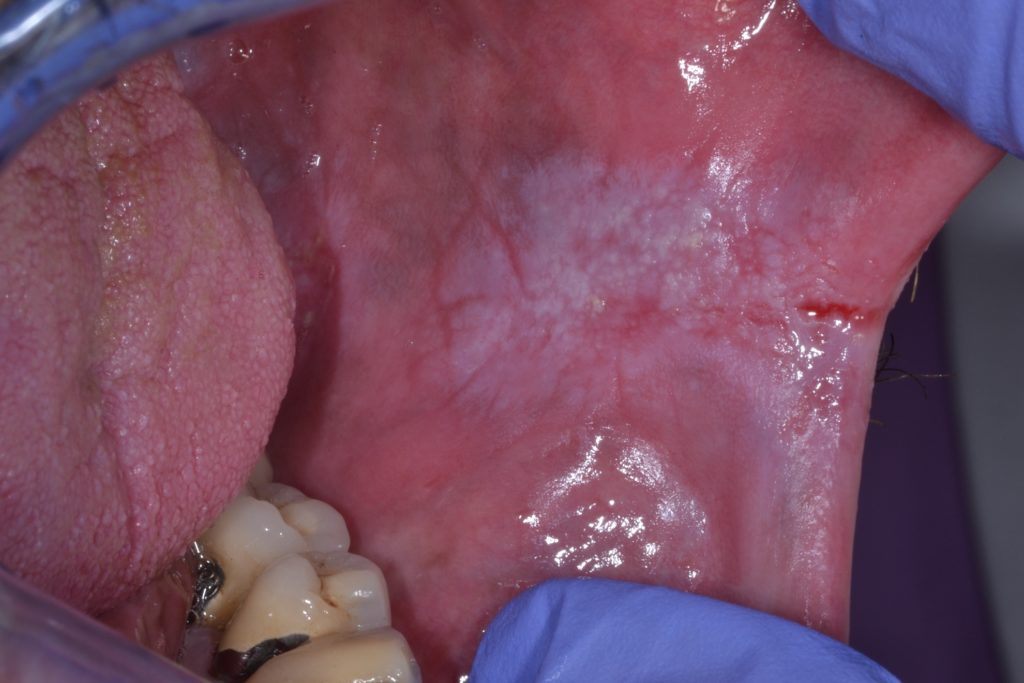
Leukoplakia is a condition that can arise due to various factors, one of the most prominent being the use of chewing tobacco. This condition manifests as white patches in the mouth, often indicating an underlying issue that requires attention. Chewing tobacco, a common habit among individuals, can lead to several oral health problems, including leukoplakia, which can sometimes progress to more serious conditions. Understanding the relationship between leukoplakia and chewing tobacco is essential for both prevention and management.
As tobacco is chewed, the mucous membranes in the mouth become irritated and damaged, leading to the formation of these white lesions. The presence of leukoplakia can serve as a warning sign, indicating that the tissues in the mouth are experiencing stress due to the harmful chemicals in tobacco. Additionally, leukoplakia is often asymptomatic, which means many people may be unaware of its presence until it is discovered during a routine dental examination.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for those who use chewing tobacco, as leukoplakia can occasionally progress to oral cancer if left unchecked. This article will delve into the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for leukoplakia resulting from chewing tobacco, emphasizing the importance of oral health and regular check-ups for tobacco users.
What is Leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia is a term used to describe white patches that form on the mucous membranes of the mouth. These patches are often painless and can vary in size. While leukoplakia itself is not cancerous, it can be a precursor to more serious conditions, including oral cancer. The exact cause of leukoplakia is not always clear, but it is frequently associated with irritants such as tobacco, alcohol, and trauma to the oral tissues.
How Does Chewing Tobacco Cause Leukoplakia?
Chewing tobacco contains numerous harmful substances that can irritate the oral mucosa. The following mechanisms explain how chewing tobacco can lead to leukoplakia:
- Irritation: Continuous irritation from the tobacco can lead to thickening of the tissue.
- Chemical Exposure: The chemicals in tobacco can cause changes in the cells of the oral lining.
- Immune Response: The body may react to the constant presence of irritants, leading to abnormal tissue growth.
What Are the Symptoms of Leukoplakia from Chewing Tobacco?
Leukoplakia is often asymptomatic; however, some individuals may experience the following symptoms:
- White patches on the gums, tongue, or inside of the cheeks
- Thickened, raised lesions
- Discomfort or sensitivity in the affected areas, particularly when consuming spicy or acidic foods
- Difficulty moving the tongue or opening the mouth in severe cases
When Should You See a Doctor for Leukoplakia?
If you notice any white patches in your mouth, especially if you are a user of chewing tobacco, it is important to seek medical advice. Regular dental check-ups can help identify leukoplakia early, allowing for timely intervention. You should see a doctor if:
- The white patches persist for more than two weeks.
- The lesions become painful or start to bleed.
- You experience difficulty swallowing or speaking.
How is Leukoplakia Diagnosed?
To diagnose leukoplakia, a healthcare provider will typically perform the following:
- Visual Examination: A thorough inspection of the mouth to identify any unusual lesions.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of tissue may be taken for laboratory analysis to rule out cancerous changes.
- Medical History: A review of the patient’s history regarding tobacco use and other potential risk factors.
What Are the Treatment Options for Leukoplakia?
Treatment for leukoplakia primarily focuses on eliminating the irritant and monitoring the condition. Here are common approaches:
- Quitting Tobacco: The most effective way to manage leukoplakia is to stop using chewing tobacco.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition and ensure it does not progress.
- Medical Treatment: In some cases, medications or topical treatments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Removal: If leukoplakia is extensive or shows signs of dysplasia, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Can Leukoplakia from Chewing Tobacco Lead to Cancer?
While leukoplakia itself is not cancerous, it can increase the risk of developing oral cancer, especially in individuals who continue to use tobacco. The presence of dysplastic cells within the leukoplakic patches can indicate a higher risk for malignant transformation. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with leukoplakia to have regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider.
How Can You Prevent Leukoplakia from Chewing Tobacco?
Prevention strategies focus largely on avoiding tobacco use and maintaining good oral hygiene:
- Quit Chewing Tobacco: Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups to quit.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to reduce the risk of irritation.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Schedule routine visits to monitor oral health.
Conclusion: Understanding the Risks of Chewing Tobacco
Leukoplakia from chewing tobacco is a significant health concern that warrants attention. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely medical advice, and taking proactive steps to quit tobacco, individuals can reduce their risk of developing leukoplakia and its potential complications. Maintaining oral health through good hygiene practices and regular check-ups is crucial in preventing the onset of this condition and safeguarding against more severe health issues.