Who Invented The Computer? A Comprehensive Look At The Pioneers Of Computing
The invention of the computer is one of the most significant milestones in human history, revolutionizing how we work, communicate, and live. Understanding who invented the computer involves delving into the contributions of several brilliant minds over centuries. In this article, we will explore the key figures and their inventions that paved the way for modern computing. From Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine to the electronic computers of the 20th century, this journey will showcase the evolution of one of humanity's greatest inventions.
The term "computer" has evolved over time, initially referring to a person who performed calculations. However, as technology progressed, it became synonymous with machines that could process data. This article will not only identify the inventors of the computer but also discuss their inventions and the context in which they developed their ideas. We will also address some common misconceptions and highlight the importance of collaboration in technological advancements.
By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of the history of computers, the individuals who played pivotal roles in their development, and how these innovations have shaped our modern world. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey through the history of computing!
Table of Contents
- 1. The Early Concepts of Computing
- 2. Charles Babbage: The Father of the Computer
- 3. Ada Lovelace: The First Programmer
- 4. Alan Turing: The Theoretical Foundation
- 5. The Evolution of Electronic Computers
- 6. Notable Early Computers and Their Inventors
- 7. The Impact of Computers on Society
- 8. Conclusion: The Legacy of Computer Innovators
1. The Early Concepts of Computing
The concept of computing dates back to ancient times, with tools such as the abacus being utilized for calculations. However, it wasn't until the 19th century that the groundwork for modern computers began to take shape. Early inventors envisioned machines that could automate calculations, leading to significant advancements in mathematics and science.
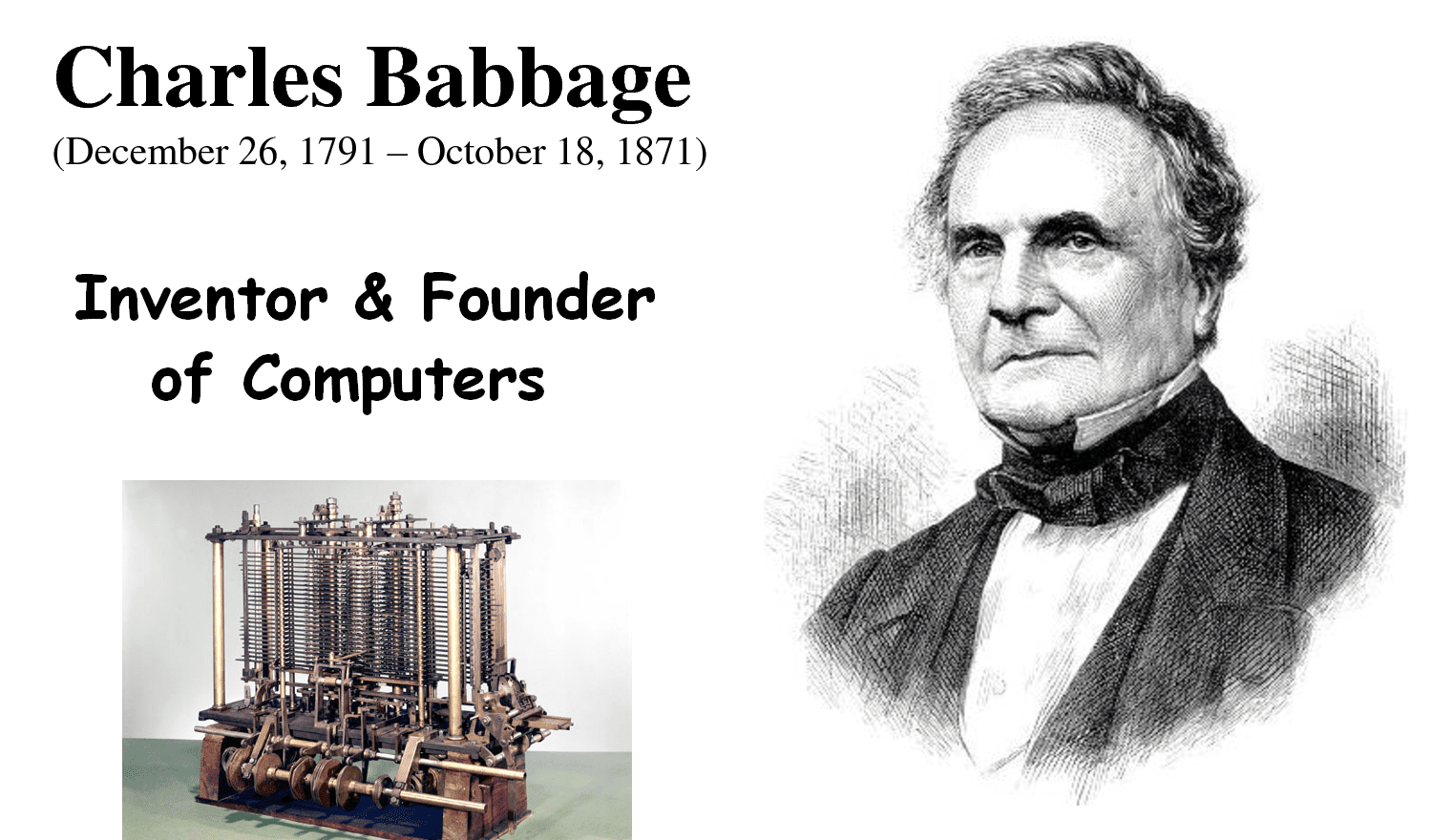
2. Charles Babbage: The Father of the Computer
Charles Babbage is often referred to as the "Father of the Computer" for his groundbreaking work on the Analytical Engine, designed in the 1830s. This machine was intended to be a general-purpose computing device capable of performing any calculation. Babbage's design included key components such as an arithmetic logic unit, control flow through conditional branching and loops, and memory.
2.1 Babbage's Contributions
- Babbage introduced the concept of programmability.
- He developed the idea of using punched cards for input and output.
- His work laid the foundation for modern computing architecture.
2.2 The Analytical Engine
The Analytical Engine was never completed during Babbage's lifetime, but his designs influenced future generations of computer scientists and engineers. In many ways, it was a vision of what computers would eventually become.
3. Ada Lovelace: The First Programmer
Ada Lovelace, a mathematician and writer, is celebrated as the first computer programmer. She worked with Babbage on the Analytical Engine and recognized its potential beyond mere calculations. Lovelace created an algorithm for the machine, which is considered the first computer program.
3.1 Lovelace's Vision
Ada Lovelace foresaw that computers could manipulate symbols and create music or art, a radical idea for her time. Her insights into computing's capabilities extended far beyond arithmetic, emphasizing the creative potential of machines.
4. Alan Turing: The Theoretical Foundation
Alan Turing, a British mathematician and logician, is regarded as one of the founding figures of computer science. His work during World War II on the Enigma machine helped lay the groundwork for modern computing. Turing introduced the concept of the Turing machine, a theoretical construct that formalized the notion of computation.
4.1 Turing's Contributions
- Developed the Turing test to assess a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior.
- His research on algorithms and computation forms the basis of computer science.
- Turing's work inspired future developments in artificial intelligence.
5. The Evolution of Electronic Computers
The transition from mechanical to electronic computers marked a significant turning point in computing history. The invention of vacuum tubes and later transistors allowed for faster and more reliable machines.
5.1 Early Electronic Computers
Key developments in early electronic computers include:
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) - the first general-purpose electronic computer.
- UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) - the first commercial computer.
- IBM's contributions to mainframe computing.
6. Notable Early Computers and Their Inventors
Several early computers made significant impacts on the development of technology. Each of these machines had distinct features and capabilities that contributed to the evolution of computing:
| Computer | Inventor(s) | Year | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENIAC | John Mauchly, J. Presper Eckert | 1945 | First general-purpose electronic computer |
| UNIVAC I | J. Presper Eckert, John Mauchly | 1951 | First commercial computer |
| IBM 701 | IBM | 1952 | First IBM computer |
7. The Impact of Computers on Society
The invention of computers has profoundly impacted society. From business and education to healthcare and entertainment, computing technology has transformed every aspect of human life. Key impacts include:
- Increased efficiency in various industries.
- Revolutionized communication and information sharing.
- Enabled advancements in science and technology.
8. Conclusion: The Legacy of Computer Innovators
In conclusion, the invention of the computer was a collaborative effort involving numerous innovators across different eras. Figures like Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing laid the foundations for the digital age we live in today. Their contributions continue to inspire future generations of scientists, engineers, and thinkers.
As we reflect on the history of computing, it's essential to appreciate the interconnectedness of these pioneering efforts. Each inventor built upon the work of others, showcasing the importance of collaboration in technological advancement. We encourage readers to share their thoughts in the comments and explore more articles on the fascinating world of technology!
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the history of computers. We hope to see you back here for more insightful discussions on technology and innovation!