Understanding The Back Of Head Muscles: Anatomy And Function
The back of head muscles play a crucial role in the movement and stability of the head and neck. Understanding these muscles is essential for anyone interested in anatomy, fitness, or rehabilitation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various muscles located at the back of the head, their functions, and their importance in daily activities. With an in-depth look at anatomy and practical implications, this article aims to provide valuable insights for both professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Muscle health is integral to maintaining posture, preventing injury, and enhancing athletic performance. The back of head muscles, including the trapezius, splenius, and semispinalis, contribute significantly to these aspects. Whether you’re a fitness professional, a student of anatomy, or simply someone eager to improve your understanding of human physiology, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need.
From understanding the anatomy to exploring exercises that target these muscles, we will cover a wide array of topics related to the back of head muscles. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of these muscles, their functions, and how to keep them healthy and strong.
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Back of Head Muscles
- Major Muscles in the Back of the Head
- Functions of Back of Head Muscles
- Common Issues and Injuries
- Exercises for Strengthening
- Stretching Techniques
- Rehabilitation for Muscle Strain
- Conclusion
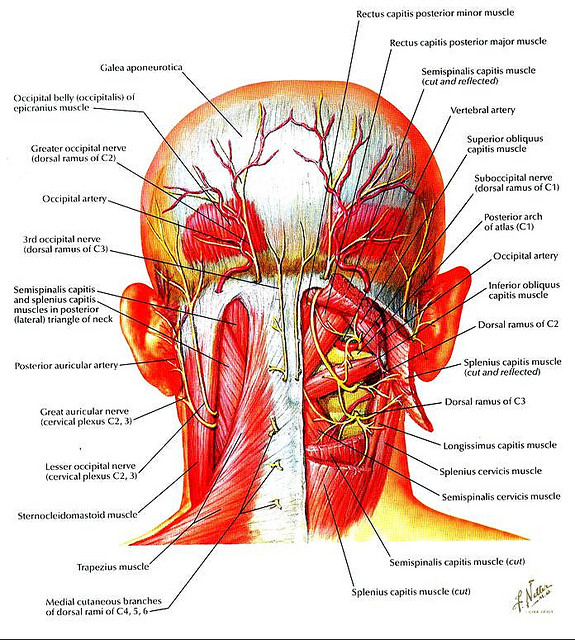
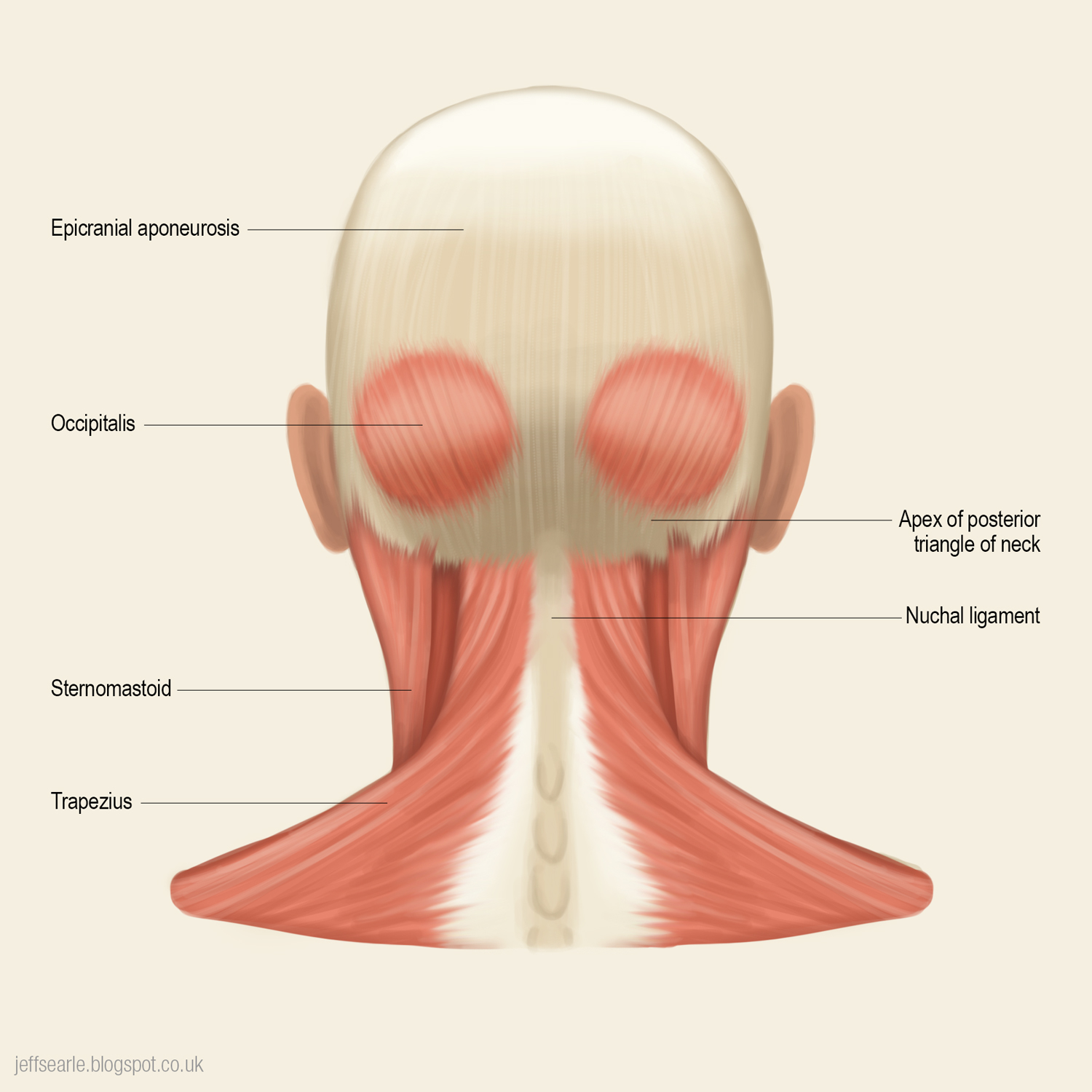
Anatomy of the Back of Head Muscles
The back of head muscles consist of various layers and groups that work together to support the head and facilitate movement. Understanding the anatomical structure of these muscles is essential for anyone studying human anatomy or involved in physical therapy.
These muscles are primarily located in the posterior region of the neck and the base of the skull. They are responsible for movements such as extension, rotation, and lateral flexion of the head. Some of the key muscles found in this area include:
- Trapezius
- Splenius Capitis
- Splenius Cervicis
- Semispinalis Capitis
- Longissimus Capitis
Major Muscles in the Back of the Head
The Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius muscle is one of the largest muscles in the back and extends from the base of the skull to the middle of the back. It plays a significant role in supporting the shoulder girdle and the head. The trapezius muscle can be divided into three parts:
- Upper Trapezius: Responsible for elevating the scapula and extending the neck.
- Middle Trapezius: Aids in retracting the scapula.
- Lower Trapezius: Assists in depression and upward rotation of the scapula.
The Splenius Muscle
The splenius muscle group consists of two muscles: the splenius capitis and splenius cervicis. These muscles are located deeper than the trapezius and are primarily responsible for the rotation and extension of the head.
- Splenius Capitis: This muscle runs from the upper thoracic and cervical vertebrae to the base of the skull, assisting in head extension and rotation.
- Splenius Cervicis: Originating from the upper thoracic vertebrae and inserting into the cervical vertebrae, it aids in neck movement and stability.
The Semispinalis Muscle
The semispinalis muscle is part of the transversospinalis group and plays a crucial role in the extension and rotation of the head and neck. It is divided into three parts:
- Semispinalis Capitis
- Semispinalis Cervicis
- Semispinalis Thoracis
This muscle group originates from the transverse processes of the vertebrae and inserts into the occipital bone, enabling a wide range of head movements.
Functions of Back of Head Muscles
The back of head muscles serve several critical functions, including:
- Supporting the head in an upright position.
- Facilitating head movements such as rotation, extension, and lateral flexion.
- Maintaining posture and alignment of the spine.
- Providing stability during various physical activities.
Common Issues and Injuries
Muscle strain and tension in the back of the head can lead to discomfort and pain. Common issues include:
- Tension headaches caused by muscle tightness.
- Neck pain from poor posture.
- Injuries due to sudden movements or overexertion.
It is essential to address these issues promptly to prevent further complications.
Exercises for Strengthening
Incorporating specific exercises can help strengthen the back of head muscles. Here are some effective exercises:
- Shoulder Shrugs: Helps strengthen the trapezius.
- Neck Rolls: Promotes flexibility and reduces tension.
- Resistance Band Pulls: Engages multiple muscle groups in the back and neck.
- Plank Variations: Strengthens core and stabilizing muscles.
Stretching Techniques
Stretching is vital for maintaining flexibility and preventing injuries. Some effective stretching techniques include:
- Chin Tucks: Helps elongate the neck muscles.
- Neck Side Bends: Stretches the lateral neck muscles.
- Upper Trapezius Stretch: Targets the trapezius muscle.
Rehabilitation for Muscle Strain
If you experience strain in the back of head muscles, it’s essential to follow a rehabilitation program. Key components include:
- Rest: Allowing the muscles to recover.
- Ice Therapy: Reduces inflammation and pain.
- Gradual Strengthening: Slowly reintroducing exercises as tolerated.
Conclusion
Understanding the back of head muscles is vital for maintaining overall health and wellness. By strengthening and stretching these muscles, individuals can improve their posture, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance their physical performance. Remember to consult a healthcare professional or a fitness expert before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing conditions or concerns.
If you found this article helpful, please consider leaving a comment below, sharing it with others, or exploring more articles on our site to expand your knowledge further.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to having you back here for more informative content!