Understanding The Carbon Number Of Protons: A Comprehensive Guide
The carbon number of protons is an essential concept in the field of chemistry, particularly in understanding the properties of carbon and its role in organic compounds. Carbon, with its unique ability to form stable bonds with various elements, serves as the backbone of life on Earth. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the carbon number of protons, its significance, and its implications in various scientific contexts.
As we explore this topic, we will discuss the atomic structure of carbon, the significance of protons in determining an element's identity, and the role carbon plays in biochemistry and environmental science. This comprehensive guide aims to provide clarity on the carbon number of protons and how it affects our understanding of chemistry and life itself.
Throughout this article, we will ensure that the information presented is accurate, well-researched, and easy to understand, adhering to the principles of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Let's embark on this journey to uncover the fascinating world of carbon and its protons.
Table of Contents
- What is Carbon?
- Understanding Atomic Structure
- The Role of Protons in Elements
- The Carbon Number of Protons Explained
- Isotopes of Carbon
- The Importance of Carbon in Biochemistry
- Carbon and Its Role in Environmental Science
- Conclusion
What is Carbon?
Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol 'C' and atomic number 6. It is a non-metal that is essential for life, forming the basis of organic chemistry. Carbon atoms can bond with other atoms in various configurations, leading to a vast array of compounds. Here are some key points about carbon:
- Carbon is found in all known life forms.
- It can form four covalent bonds with other elements.
- Carbon compounds include hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids.
Understanding Atomic Structure
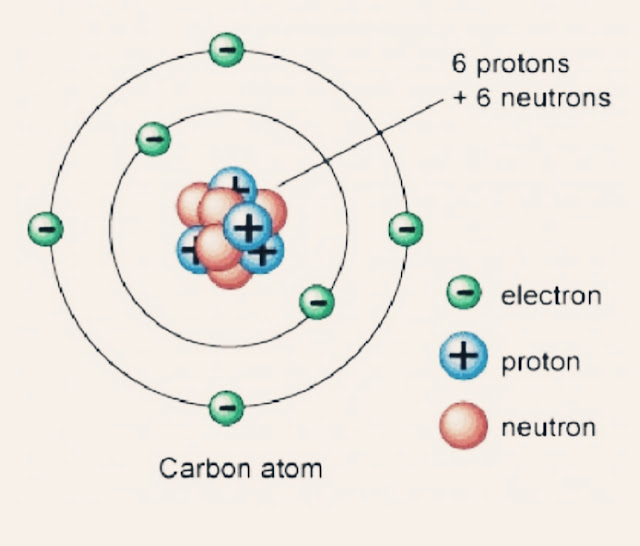
The atomic structure of an element comprises protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom defines the element itself, known as the atomic number.
Components of Atomic Structure
Here’s a breakdown of the components of atomic structure:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles that also reside in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
The Role of Protons in Elements
Protons play a crucial role in determining the identity of an element. The number of protons in the nucleus is what distinguishes one element from another. For instance:
- Hydrogen has 1 proton.
- Helium has 2 protons.
- Carbon, as mentioned, has 6 protons.
Thus, the carbon number of protons, which is 6, is fundamental in categorizing carbon as a distinct element on the periodic table.
The Carbon Number of Protons Explained
The carbon number of protons is specifically defined as 6. This number is significant for several reasons:
- It determines carbon's position in the periodic table.
- It influences the chemical behavior of carbon.
- It is essential for understanding carbon's isotopes and their applications.
Isotopes of Carbon
Carbon has several isotopes, which are variants of carbon that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The most notable isotopes of carbon include:
- Carbon-12: The most abundant isotope, with 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
- Carbon-13: A stable isotope, with 6 protons and 7 neutrons.
- Carbon-14: A radioactive isotope, used in radiocarbon dating, with 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
The Importance of Carbon in Biochemistry
Carbon is often referred to as the "building block of life" due to its ability to form complex molecules. Here are some of the ways carbon is vital in biochemistry:
- It forms the backbone of macromolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
- Carbon's tetravalent nature allows for diverse chemical structures.
- It plays a key role in metabolic processes, including cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Carbon and Its Role in Environmental Science
In environmental science, carbon is a critical element in understanding climate change and ecological balance. Here are some points on its significance:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
- Carbon cycling is essential for ecosystem sustainability.
- Carbon sequestration techniques are being researched to mitigate climate change.
Conclusion
In summary, the carbon number of protons is a fundamental aspect of chemistry that defines carbon's identity and its significance in various scientific fields. Understanding carbon and its unique properties helps us appreciate its role in life and the environment. We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring other related articles on our site.
Thank you for taking the time to learn about the carbon number of protons. We hope you found this guide informative and valuable. Don't forget to visit us again for more insightful articles!