What Causes HCG Levels To Rise If Not Pregnant?
Understanding the reasons behind elevated HCG levels when pregnancy is not present is crucial for many individuals. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone primarily associated with pregnancy, but its presence in non-pregnant individuals can indicate various underlying health conditions. This article delves into the causes of elevated HCG levels, providing valuable insights for those navigating this complex health topic.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the science behind HCG, the potential conditions that can lead to increased levels, and the importance of understanding these changes. Whether you are a medical professional, someone facing health concerns, or simply curious about the topic, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge you need.
Join us as we uncover the multifaceted reasons behind rising HCG levels outside of pregnancy, offering a detailed look into this critical health marker.
Table of Contents
- Understanding HCG
- Normal HCG Levels
- Causes of Elevated HCG Levels
- HCG Levels and Health Conditions
- HCG and Tumors
- HCG in Men
- Diagnosing Elevated HCG Levels
- Conclusion
Understanding HCG
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. It plays a vital role in maintaining the pregnancy and is the hormone detected by most pregnancy tests. Elevated HCG levels are commonly associated with pregnancy, but they can also occur in non-pregnant individuals under certain circumstances.
HCG is composed of two subunits, alpha and beta, with the beta subunit being unique to HCG and used to confirm pregnancy. Understanding how HCG works and its normal levels can help in identifying the causes of abnormal elevations.
Normal HCG Levels
Normal HCG levels vary based on gender and pregnancy status. In women, normal HCG levels vary significantly in early pregnancy, from 5 to 50 mIU/mL in the first few weeks, and can reach over 100,000 mIU/mL by the end of the first trimester. For non-pregnant women, HCG levels are typically less than 5 mIU/mL. In men, normal HCG levels are also low, generally under 2.5 mIU/mL.
Causes of Elevated HCG Levels
When HCG levels rise in non-pregnant individuals, it can be due to several factors:
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: A group of rare tumors that involve abnormal growth of cells inside a woman's uterus.
- Ovarian Cysts: Certain types of ovarian cysts can produce HCG.
- Hormonal Disorders: Conditions such as pituitary tumors can lead to increased HCG production.
- Medications: Some fertility treatments and medications can cause elevated HCG levels.
HCG Levels and Health Conditions
Elevated HCG levels can be indicative of several health conditions that may require medical attention:
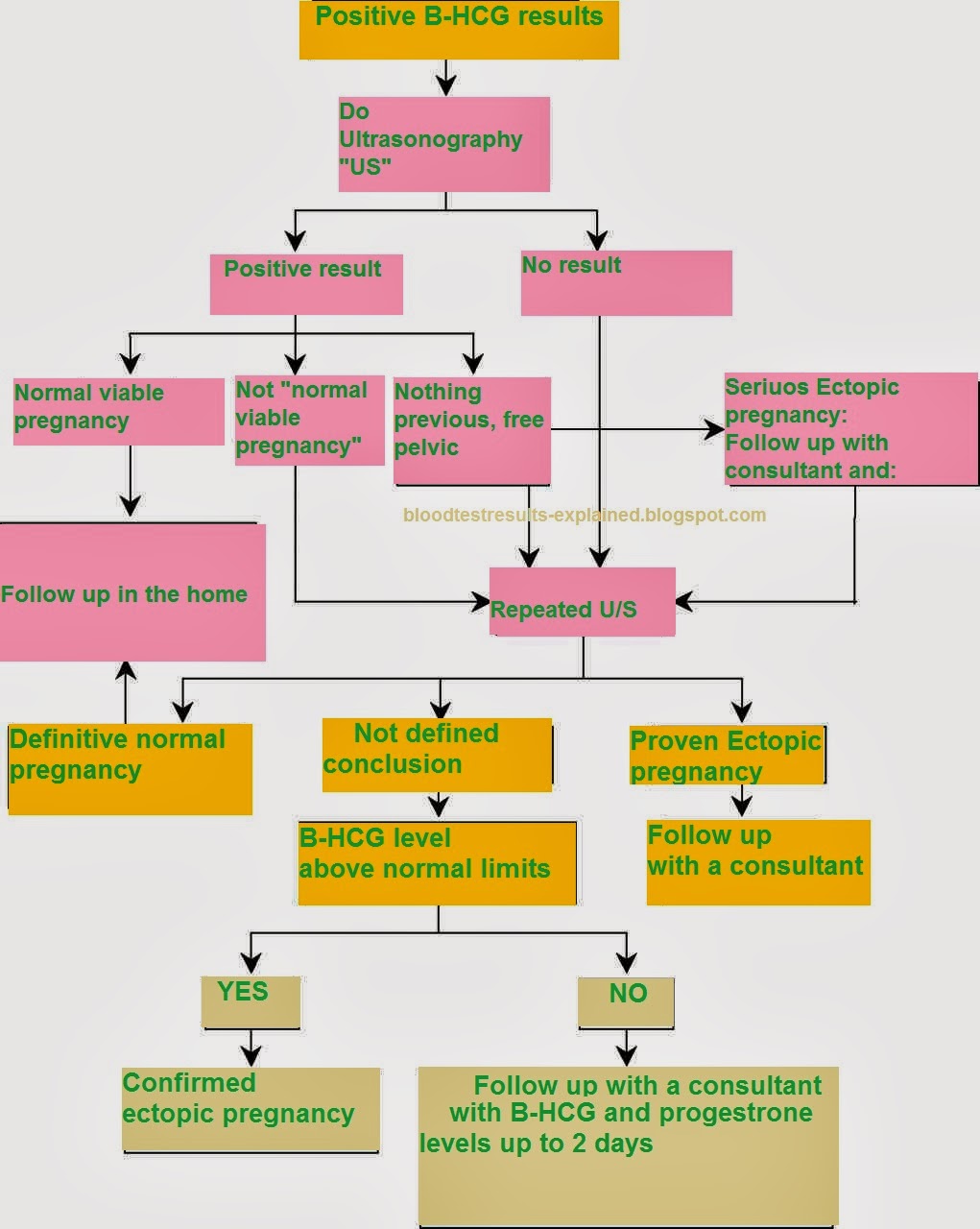
1. Ectopic Pregnancy
This is a serious condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube, leading to elevated HCG levels without a viable pregnancy.
2. Testicular Cancer
In men, certain types of testicular cancer can result in increased HCG levels, making it a marker for diagnosis.
3. Liver Disease
Some liver diseases can also cause elevated HCG levels, complicating the diagnosis and management of the condition.
HCG and Tumors
Tumors, particularly those associated with the reproductive system, can produce HCG. This includes:
- Choriocarcinoma: A fast-growing cancer that can occur in the uterus.
- Yolk Sac Tumors: A type of germ cell tumor that can produce HCG.
HCG in Men
While HCG is primarily associated with women, men can also experience elevated levels due to various causes:
- Testicular Cancer: As mentioned earlier, specific tumors can lead to increased HCG production.
- Hyperthyroidism: This condition can sometimes cause elevated HCG levels in men.
Diagnosing Elevated HCG Levels
Diagnosing the cause of elevated HCG levels typically involves a combination of:
- Blood tests to measure HCG levels.
- Imaging studies such as ultrasounds to assess reproductive organs.
- A thorough medical history and physical examination.
Conclusion
In summary, elevated HCG levels in non-pregnant individuals can be attributed to various health conditions, including tumors, hormonal disorders, and certain medications. Understanding these causes is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. If you suspect elevated HCG levels, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and evaluation.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, and feel free to explore our other articles for more health-related information.
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into the causes of elevated HCG levels when not pregnant. Stay informed and healthy!