What Was The Book Of The Dead? Unraveling Ancient Egyptian Mysteries
The Book of the Dead is one of the most significant texts from ancient Egypt, representing the beliefs, rituals, and cultural framework of a civilization that has fascinated historians and archaeologists for centuries. This ancient manuscript served as a guide for the deceased in the afterlife, providing insights into the spiritual practices and beliefs of the Egyptian people. In this article, we will delve into the origins, content, and significance of the Book of the Dead, exploring its role in ancient Egyptian funerary practices and its lasting impact on modern understanding of ancient cultures.
The Book of the Dead, known in ancient Egyptian as "The Book of Coming Forth by Day," was a compilation of spells, prayers, and incantations intended to assist the deceased in navigating the afterlife. This text was not a single book but rather a collection of various writings that evolved over time, with each version tailored to the individual needs of the deceased. From the Old Kingdom to the New Kingdom, the Book of the Dead underwent significant changes, reflecting the shifting beliefs and practices related to death and the afterlife in ancient Egypt.
Throughout the article, we will explore the historical context of the Book of the Dead, its various components, and how it has been preserved through the ages. By examining this remarkable text, we can gain a better understanding of the complex beliefs that shaped ancient Egyptian society and their views on life, death, and the afterlife.
Table of Contents
- 1. Historical Context of the Book of the Dead
- 2. The Structure and Components of the Book of the Dead
- 3. Key Spells and Their Significance
- 4. The Role of the Book of the Dead in Funerary Practices
- 5. Variations in the Book of the Dead Across Time
- 6. The Book of the Dead in Modern Culture
- 7. Preservation and Discoveries of the Book of the Dead
- 8. Conclusion: The Ongoing Legacy of the Book of the Dead
1. Historical Context of the Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead emerged during a time of profound transformation in ancient Egyptian society. Its origins can be traced back to the Old Kingdom (c. 2686–2181 BCE) when the Pyramid Texts, which were inscribed in royal tombs, served similar purposes. However, as the society evolved and the concept of the afterlife became more accessible to the general populace, the Book of the Dead began to take shape.
This transition coincided with the rise of the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BCE) when the belief that everyone could achieve a pleasant afterlife became more prevalent. The spells and prayers contained within the Book of the Dead were crafted to assist not only the elite but also ordinary individuals in their journey to the afterlife.
2. The Structure and Components of the Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead is not a singular text but rather a compilation of various spells and incantations. These texts were often written on papyrus scrolls and placed in the tombs of the deceased. The structure of the Book of the Dead can be categorized into several key components:
- **Introduction**: The opening sections typically include a series of spells intended to prepare the deceased for their journey.
- **Spells for Protection**: Many spells focus on providing protection against malevolent forces in the afterlife.
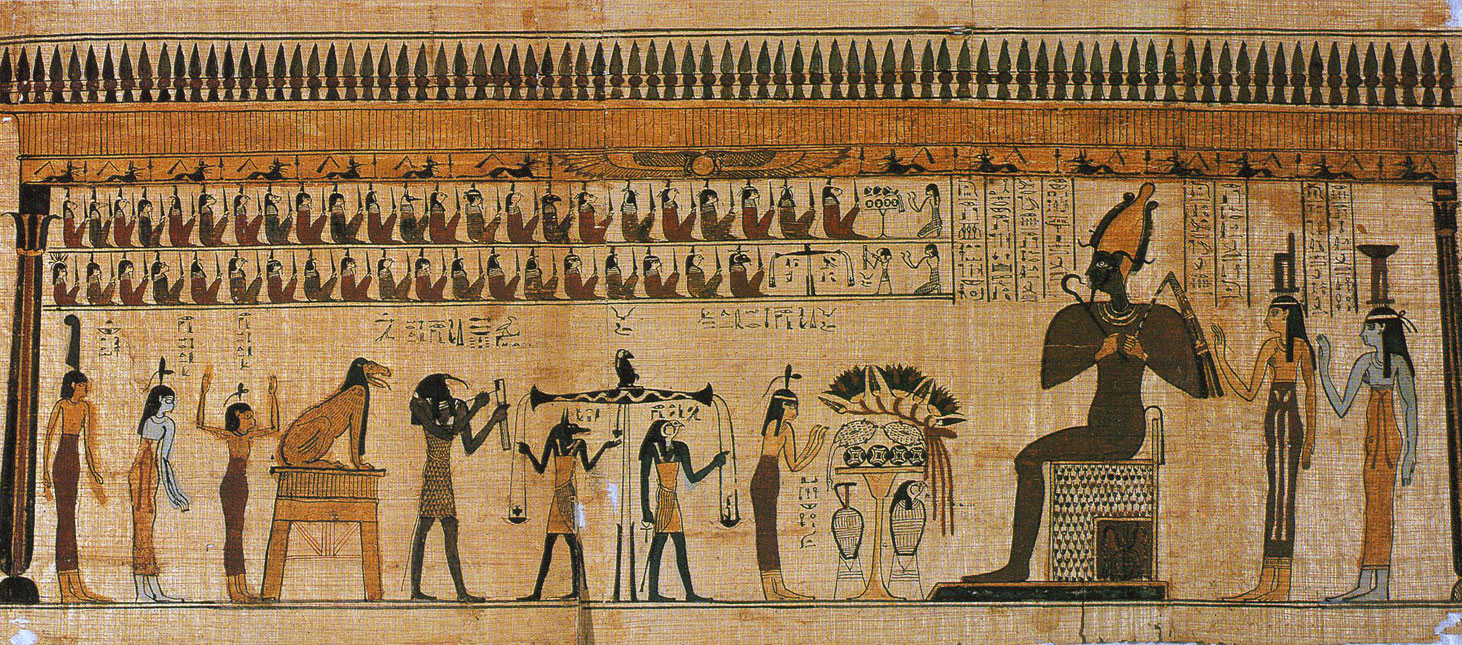
- **Judgment Scenes**: These spells describe the weighing of the heart ceremony, where the deceased's heart is weighed against the feather of Ma'at, representing truth and justice.
- **Hymns and Prayers**: The Book of the Dead also contains hymns and prayers aimed at deities to seek favor and assistance in the afterlife.
2.1 Different Versions of the Book of the Dead
Over time, various versions of the Book of the Dead emerged, with each individual customizing their texts according to their beliefs and desires. The most famous version, known as the “Papyrus of Ani,” dates back to the New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BCE) and is one of the best-preserved examples.
2.2 The Role of Illustrations
Many copies of the Book of the Dead feature colorful illustrations that depict scenes from the afterlife, including the deceased interacting with gods and undergoing judgment. These images were intended to provide additional guidance and support to the deceased on their spiritual journey.
3. Key Spells and Their Significance
Among the many spells found in the Book of the Dead, several stand out for their importance in ancient Egyptian belief systems:
- **Spell 125**: This is perhaps the most famous spell, detailing the judgment of the deceased before Osiris, the god of the afterlife. It describes the weighing of the heart against the feather of Ma'at.
- **Spell 1**: This spell serves as an introduction, calling upon various deities to assist the deceased on their journey.
- **Spell 30B**: A protective spell that ensures the deceased's safe passage through the Duat, the Egyptian underworld.
4. The Role of the Book of the Dead in Funerary Practices
The Book of the Dead played a crucial role in ancient Egyptian funerary practices. It was believed that the spells contained within the text would provide the necessary guidance for the deceased to navigate the afterlife successfully. The Book was often buried with the deceased, either written on a papyrus scroll or inscribed on tomb walls.
Funeral rituals often included the recitation of selected spells to ensure the deceased's protection and successful transition into the afterlife. These rituals were typically performed by priests, who acted as intermediaries between the living and the divine.
5. Variations in the Book of the Dead Across Time
As ancient Egyptian beliefs evolved, so did the Book of the Dead. Different dynasties produced variations that reflected changing theological and cultural perspectives. For instance, during the New Kingdom, the text became more elaborate, with increased emphasis on providing comfort and assurance to the deceased.
Regional differences also influenced the content and structure of the Book of the Dead. For example, some texts from the Theban region included unique spells not found in other versions, highlighting the diversity of beliefs within ancient Egypt.
6. The Book of the Dead in Modern Culture
The Book of the Dead has left a lasting legacy in modern culture. Its themes of death, the afterlife, and spiritual guidance continue to resonate today. The text has inspired countless adaptations in literature, film, and art, reflecting humanity's ongoing fascination with ancient Egyptian beliefs.
Moreover, scholars and Egyptologists continue to study the Book of the Dead to gain insights into ancient Egyptian society, religion, and culture. Its relevance persists in academic circles, providing a window into the spiritual world of one of history's most enduring civilizations.
7. Preservation and Discoveries of the Book of the Dead
Preserving the Book of the Dead has been a challenge due to the fragility of ancient materials. However, numerous discoveries have been made over the years, leading to the recovery of significant texts and artifacts.
Some of the most notable discoveries include:
- The **Papyrus of Ani**, housed in the British Museum, is one of the most complete versions of the Book of the Dead.
- Various tombs in the Valley of the Kings have revealed inscriptions and scrolls that provide invaluable insights into funerary practices.
- Recent archaeological efforts continue to uncover new texts and artifacts, expanding our understanding of this ancient tradition.
8. Conclusion: The Ongoing Legacy of the Book of the Dead
In summary, the Book of the Dead is a remarkable testament to the beliefs and practices of ancient Egypt, reflecting their views on life, death, and the afterlife. Its spells and illustrations provide a fascinating glimpse into the spiritual world of this ancient civilization.
As we continue to study and uncover the mysteries of the Book of the Dead, we invite you to share your thoughts in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others or exploring more content on our site.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the ancient world, and we hope to see you back again soon for more captivating explorations!