Understanding Semantic And Syntactic: The Foundations Of Language Processing
Semantic and syntactic play crucial roles in the field of linguistics and natural language processing. These concepts help us understand how language works, how meaning is derived from sentences, and how computers can analyze human language. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, differences, and applications of semantic and syntactic analysis. Additionally, we will explore their significance in various fields, including artificial intelligence and linguistics.
As technology continues to evolve, the importance of semantic and syntactic analysis has grown exponentially. From chatbots to translation services, understanding the nuances of language is essential for creating systems that can effectively communicate with humans. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these two fundamental aspects of language.
Whether you are a student, a professional in the tech industry, or simply curious about how language works, this article will equip you with valuable insights into the world of semantic and syntactic analysis. Let’s embark on this linguistic journey and explore the fascinating interplay between meaning and structure in language.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Semantic and Syntactic
- Importance of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
- Differences Between Semantic and Syntactic
- Applications of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
- Challenges in Semantic and Syntactic Processing
- The Future of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
- Conclusion
- References
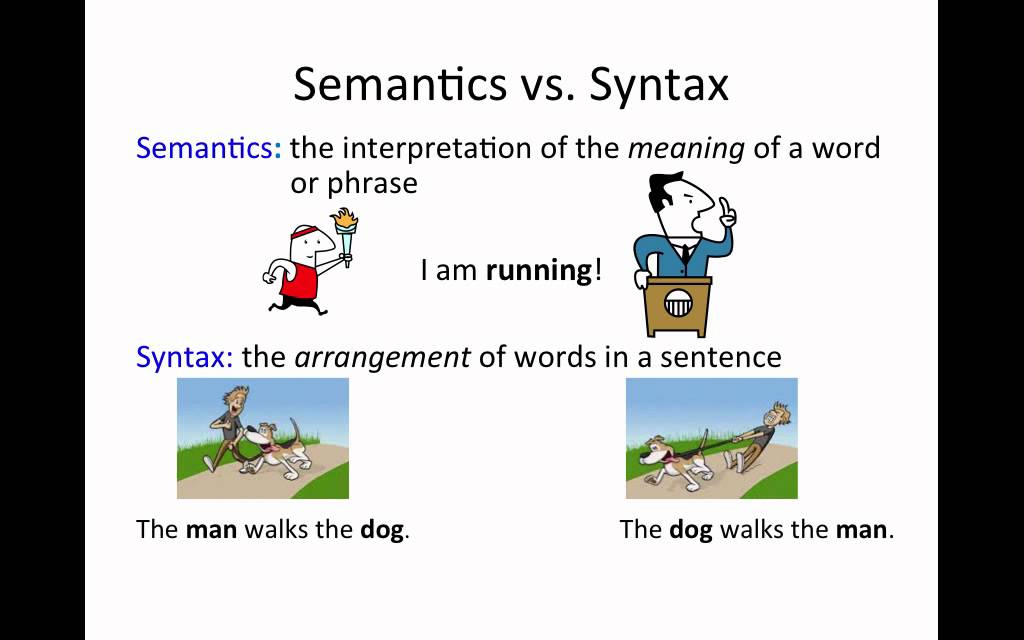
Definition of Semantic and Syntactic
Syntactic refers to the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language. It involves the rules and structures that dictate how sentences are constructed. For example, in English, a basic syntactic structure follows the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) order, as in "The cat (subject) chased (verb) the mouse (object)." Understanding syntax is crucial for parsing sentences and analyzing grammatical relationships.
On the other hand, semantic pertains to the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It focuses on how language conveys meaning and how the interpretation of that meaning can vary based on context. For instance, the sentence "The cat is on the mat" conveys a specific meaning based on the words used, while the sentence "The cat is a mat" carries a different meaning due to the change in syntax and the relationships between the words.
Key Components of Semantic
- Lexical Semantics: Study of word meanings and their relationships.
- Compositional Semantics: How meanings combine in phrases and sentences.
- Pragmatics: Contextual meaning and how language is used in practice.
Key Components of Syntactic
- Parts of Speech: Categories of words like nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.
- Phrase Structure: The organization of words into phrases and clauses.
- Grammar Rules: Guidelines that define how sentences are constructed.
Importance of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
Understanding both semantic and syntactic analysis is crucial for several reasons:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): These analyses are foundational for NLP tasks such as machine translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbot development.
- Effective Communication: Recognizing the structure and meaning of sentences enhances our ability to communicate clearly and effectively.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Semantic analysis helps search engines understand content better, improving search results and user experience.
Differences Between Semantic and Syntactic
While semantic and syntactic are interconnected, they have distinct differences:
- Focus: Syntactic focuses on structure, while semantic focuses on meaning.
- Analysis: Syntactic analysis examines the grammatical correctness of a sentence, while semantic analysis evaluates the meaning and context.
- Errors: Syntactic errors (e.g., incorrect word order) may lead to ungrammatical sentences, while semantic errors (e.g., ambiguous meanings) can lead to misinterpretations.
Applications of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
Semantic and syntactic analysis have a wide range of applications across various fields:
1. Artificial Intelligence
In AI, these analyses help improve machine learning algorithms, enabling systems to understand and generate human language more effectively. For instance, chatbots utilize both semantic and syntactic analysis to engage in meaningful conversations with users.
2. Linguistics
In linguistics, researchers study semantic and syntactic structures to better understand language acquisition, language evolution, and communication patterns. These studies contribute to our knowledge of how different languages function.
3. Search Engines
Search engines like Google employ semantic analysis to improve search accuracy. By understanding user intent and context, search engines can deliver more relevant results based on the meaning of search queries rather than just matching keywords.
4. Translation Services
Translation services utilize both syntactic and semantic analysis to ensure accurate and meaningful translations between languages. Understanding sentence structure and word meaning is essential for producing high-quality translations.
Challenges in Semantic and Syntactic Processing
Despite the advancements in technology, semantic and syntactic processing still face several challenges:
- Ambiguity: Natural language is often ambiguous, making it difficult for machines to interpret meaning accurately.
- Contextual Understanding: Machines may struggle to grasp context, which is essential for accurate semantic analysis.
- Language Variability: Different languages have unique syntactic structures and semantic conventions, posing challenges for universal applications.
The Future of Semantic and Syntactic Analysis
The future of semantic and syntactic analysis looks promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence and natural language processing. As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, we can expect:
- Enhanced accuracy in language understanding and generation.
- Improved contextual awareness in chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Greater integration of semantic and syntactic analysis in various applications, leading to more intuitive user experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, semantic and syntactic analysis are fundamental components of language processing that play a vital role in understanding how language works. These analyses are essential for various applications, including artificial intelligence, linguistics, and search engine optimization. By recognizing the differences and interconnections between semantic and syntactic, we can enhance our communication skills and improve our engagement with technology.
We invite you to share your thoughts on semantic and syntactic analysis in the comments below. If you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others or exploring more of our content.
References
- Jurafsky, D., & Martin, J. H. (2020). Speech and Language Processing. Pearson.
- Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic Structures. Mouton.
- Gruber, J. S. (1965). Studies in Lexical Relations. MIT Press.
- Manning, C. D., & Schütze, H. (1999). Foundations of Statistical Natural Language Processing. MIT Press.