Understanding IP To Domain Name: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of the internet, understanding the connection between IP addresses and domain names is essential for both novice and seasoned users. The IP to domain name conversion is a fundamental aspect of how we navigate the online world. This article will delve into the intricacies of IP addresses, domain names, and the processes that link them, providing you with the knowledge to enhance your digital literacy.
This guide will explain the significance of IP addresses and domain names, their functions, and the technology that facilitates their interaction. Whether you are managing a website, studying computer science, or simply curious about how the internet works, this article aims to equip you with the expertise you need.
We will explore various technical aspects, including DNS (Domain Name System), reverse DNS lookup, and the importance of reliable domain registration. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how IP addresses and domain names work together to create the seamless browsing experience we often take for granted.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is an IP Address?
- 2. What is a Domain Name?
- 3. The Relationship Between IP and Domain Name
- 4. The DNS System
- 5. Reverse DNS Lookup
- 6. Importance of Domain Registration
- 7. Common Misconceptions
- 8. Conclusion
1. What is an IP Address?
An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique string of numbers separated by periods (IPv4) or colons (IPv6) that identifies each computer using the Internet Protocol to communicate over a network. IP addresses serve two main functions: they are used for identifying the host or network interface and for providing the location of the device in the network.
- IPv4: The most widely used IP address format, consisting of four numbers ranging from 0 to 255. For example: 192.168.1.1.
- IPv6: A newer format designed to replace IPv4 due to the limited number of available addresses, consisting of eight groups of hexadecimal numbers. For example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
2. What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is a human-readable address used to access websites. It is the address users type into their web browsers to visit a specific site. Domain names are made up of two main parts: the second-level domain (SLD) and the top-level domain (TLD). For example, in the domain name "example.com," "example" is the SLD, and ".com" is the TLD.
Key Components of a Domain Name
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): Represents the specific entity or organization.
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): Indicates the type of organization or country code, such as .org, .net, or .us.
3. The Relationship Between IP and Domain Name
The relationship between IP addresses and domain names is established through the Domain Name System (DNS). When a user types a domain name into their browser, the DNS translates that domain name into the corresponding IP address, allowing the browser to locate and connect to the server hosting the website.
How IP and Domain Name Work Together
This conversion process involves several steps:
- The user enters a domain name into their browser.
- The browser sends a request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name.
- The DNS server retrieves the corresponding IP address and sends it back to the browser.
- The browser connects to the server using the IP address and loads the website.
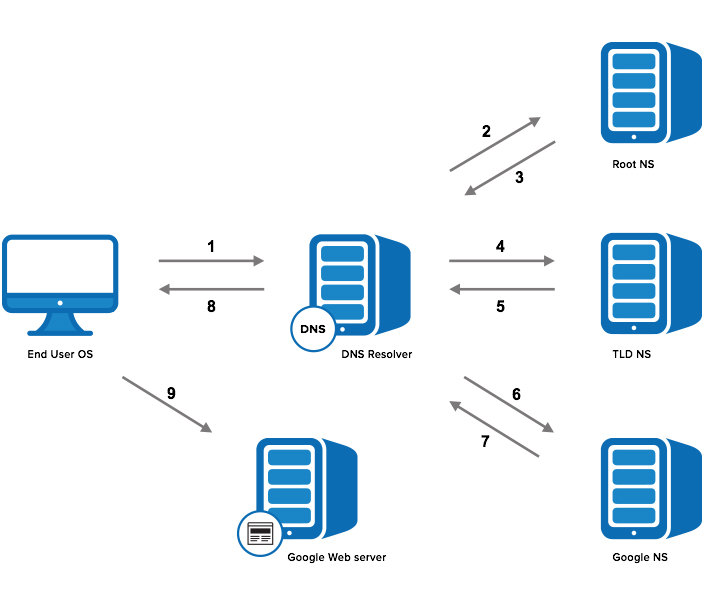
4. The DNS System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical system that translates human-friendly domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. It acts as the phonebook of the internet, allowing users to access websites without needing to remember numerical IP addresses.
Components of the DNS System
- DNS Resolver: The server that receives requests from users and queries the DNS hierarchy to find the IP address.
- Root Name Servers: The top-level servers that direct queries to the appropriate TLD servers.
- TLD Name Servers: Servers that manage the top-level domains and direct requests to the associated SLD servers.
- Authoritative Name Servers: Servers that hold the DNS records for specific domain names.
5. Reverse DNS Lookup
Reverse DNS lookup is the process of determining the domain name associated with a given IP address. This is the opposite of the standard DNS lookup, where a domain name is resolved to an IP address.
Uses of Reverse DNS Lookup
- Identifying the Owner: Helps in determining the owner of an IP address, useful for network management.
- Spam Detection: Assists in identifying spam emails by checking if the sender's IP address matches the domain name.
6. Importance of Domain Registration
Domain registration is the process of acquiring a domain name from a domain registrar. It is crucial for establishing an online presence and ensuring that your brand is recognizable and accessible on the internet.
Benefits of Domain Registration
- Brand Identity: A registered domain name enhances your brand's credibility and professionalism.
- Online Presence: It provides a unique address for users to find your business or website.
- SEO Advantages: A relevant domain name can contribute to better search engine rankings.
7. Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about IP addresses and domain names that can lead to confusion:
- All IP Addresses are Static: Not all IP addresses are static; many are dynamic and can change over time.
- Domain Names are Free: While some domain names can be obtained for free, most require registration fees.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the connection between IP addresses and domain names is vital for anyone engaging with the internet. The seamless interaction facilitated by DNS allows users to navigate the web easily, enhancing their online experience. We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, and feel free to explore our other articles for more insights into the digital world.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more informative content!