Total Iron Binding Capacity High: Understanding Its Implications For Health
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) high is a medical term that refers to the measurement of the blood's capacity to bind and transport iron. This condition can indicate various health issues, ranging from nutritional deficiencies to chronic diseases. Understanding TIBC is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients, as it can provide essential insights into an individual's iron metabolism and overall health status.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Total Iron Binding Capacity, exploring its significance, causes of elevated levels, symptoms, and management strategies. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a better understanding of how high TIBC values can affect your health and what steps you can take to address any underlying issues.
As we navigate through this topic, we will also highlight the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment options. The information provided herein is meant to serve as a valuable resource for educating readers about TIBC and its impact on health.
Table of Contents
- What is Total Iron Binding Capacity?
- Importance of TIBC in Health Assessments
- Causes of High Total Iron Binding Capacity
- Symptoms Associated with High TIBC
- Diagnosis and Testing for TIBC
- Treatment Options for High TIBC
- Preventive Measures to Maintain Normal TIBC
- Conclusion
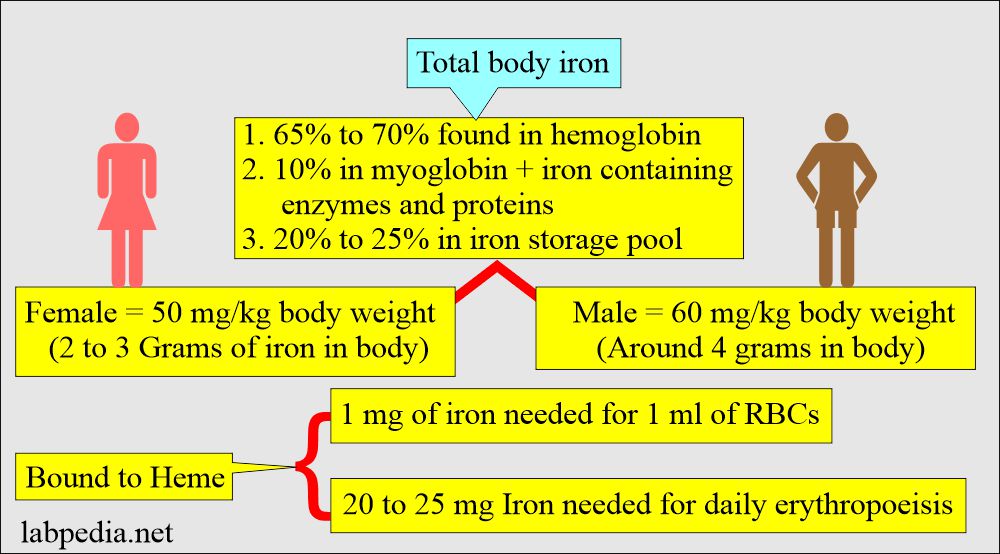
What is Total Iron Binding Capacity?
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) is a blood test that measures the blood's capacity to bind iron with transferrin, a protein that transports iron in the bloodstream. TIBC is an important indicator of iron status in the body. It helps assess how well iron is being transported and utilized, which is essential for the production of red blood cells and overall metabolic functions.
The normal range for TIBC is typically between 240 to 450 micrograms per deciliter (mcg/dL). However, these values may vary based on factors such as age, gender, and overall health. When TIBC levels are high, it indicates that there is a low concentration of iron in the blood, prompting the body to increase the production of transferrin to transport available iron more efficiently.
Importance of TIBC in Health Assessments
TIBC is a crucial component of iron studies, which also include serum iron and ferritin levels. Together, these tests provide a comprehensive picture of an individual’s iron metabolism. Understanding the significance of TIBC can help healthcare providers diagnose various conditions, including:
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Chronic blood loss
- Chronic diseases affecting iron metabolism
Monitoring TIBC levels can also assist in evaluating the effectiveness of treatments for iron deficiency and other related conditions.
Causes of High Total Iron Binding Capacity
High TIBC levels can arise from a variety of factors, including:
- Iron Deficiency: The most common cause of elevated TIBC is iron deficiency, which can occur due to inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption, or chronic blood loss.
- Pregnancy: Increased demand for iron during pregnancy can lead to higher TIBC levels, as the body attempts to transport more iron to support fetal development.
- Chronic Inflammatory Conditions: Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can affect iron metabolism and lead to elevated TIBC.
- Hypoproteinemia: Low levels of proteins in the blood can enhance TIBC as the body attempts to compensate for the deficiency.
Symptoms Associated with High TIBC
While high TIBC itself may not cause symptoms, the underlying conditions associated with it can lead to various health issues. Symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience these symptoms, as they may indicate an underlying iron deficiency or other health issues that require attention.
Diagnosis and Testing for TIBC
To diagnose high TIBC, healthcare providers will typically perform a series of blood tests, including:
- Serum Iron Test: Measures the amount of circulating iron in the blood.
- Ferritin Test: Assesses the stored iron in the body.
- TIBC Test: Measures the total iron binding capacity of the blood.
These tests are usually conducted together to provide a comprehensive view of an individual's iron status and help identify any potential deficiencies or excesses.
Treatment Options for High TIBC
Treatment for high TIBC primarily involves addressing the underlying cause of iron deficiency or the associated condition. Some common treatment options may include:
- Iron Supplements: Oral or intravenous iron supplements may be prescribed to replenish iron levels.
- Dietary Changes: Increasing iron-rich foods such as red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and fortified cereals can help improve iron intake.
- Management of Chronic Conditions: Addressing underlying chronic diseases is crucial to managing TIBC levels effectively.
Preventive Measures to Maintain Normal TIBC
To maintain normal TIBC levels and overall iron health, individuals can adopt several preventive measures:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in iron and vitamin C to enhance iron absorption.
- Monitor and manage chronic health conditions with the guidance of healthcare professionals.
- Get regular blood tests to assess iron levels, especially if you are at risk for deficiency.
Conclusion
High Total Iron Binding Capacity can be indicative of underlying health issues related to iron metabolism. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively. If you suspect that you may have high TIBC, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
We encourage you to leave your comments below, share this article with others, and explore more of our resources on health and wellness.
References
- National Institutes of Health. (2021). Iron Status and Iron Deficiency. Retrieved from [NIH Website]
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Iron Deficiency Anemia: Symptoms and Causes. Retrieved from [Mayo Clinic Website]
- World Health Organization. (2020). Nutritional Anemia. Retrieved from [WHO Website]